Chai Kim Seng 0307927
Before I start the topic I
want to explain about economic. What is economic? Many people will make a chain
between the economic and money. They think that all of economic is about the
money. Well , this is true. Economic is talking about how much do people earn,
how much they will spend, what the item cost, how much profit firm will make,
the total amount of the money there is in the economy. Money is only the
important in economic because it allow us to do things. Money is the tool and
the economic is study the money. The topic that I want to write is supply and
demand. In this supply and demand there are included quantity supplies,
quantity demand and so on. Now I want to explain each of them. Supply and
demand is perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics and it is
the backbone of a market economy.(Reem.H ,2013)
Now I want to explain the
supply first. Supply is related with the cost. When the cost was low, the
supply will increase. Supply also refers to the entire relationship between prices
and the quantity of the product supplied at each of these prices(John. B,
2008). The cost will effect by the
resources when the resources are less than the cost will be increase and supply
will decrease. In economic it makes the supply relationship the quantity of the
service or goods. More precisely and formally supply can be thought of as
"there is a given price for purchase the total quantity of a good or
service”. Supply not only simple is the
number of an item in the stock for example 5 apples or 15 cars. This is because
supply has a relationship with the quantity for sales and with all possible
prices.
The specific quantity desired to sell of a good at a
given price is known as the quantity supplied. Now I want to show you the
example of quantity when the price of an apple is 90 cents, the quantity
supplied are 350 apples a week. In this we can know that quantity supply is the
good of sale in a period. Beside that quantity supply also refers to the
particular point on the supply curve but not the entire curve. In other hand ,
quantity supply is refers to of the product is supplied at one particular price
and it is the horizontal distance between the vertical axis and the supply
curve(John .B , 2008). I want to show out two figure the explain out the
different between the supply and quantity supply.
(figure 1.1) (Conservapedia,2010)In this figure it show out
that shift of the supply curve. In this curve we can know that cost increase
the curve of the supply will decrease. In the opposite, when the cost decrease
the supply wil increase. First when increase in the supply it shift like the
the figure show (S0 shift to S2)which is
the right. In other hand, while there is decrease in the supply it will
shift to the left as the figure show(S0 to S1), from right to left. This is the
shifting of the supply.
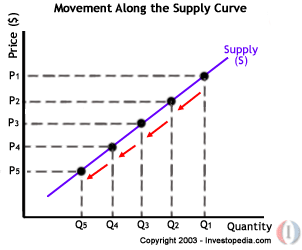
figure (1.2) (Reem.H ,
2013)This figure show out that the moving point of the quantity supply in the
curve. In this figure we can know that the quantity supply is relationship with
the price. When the price increase the quantity supply will increase also. In
other hand which mean when the price decreases the quantity supply will
decrease also. Now I want to explain about the movement of the point of
quantity supply. The point of the quantity supply is move along the curve. When
the price increases the quantity supply increase, the point of quantity supply
will move to the upward. For the opposite, when the price decreases, the
quantity supply will decrease and the point of the quantity supply will move to
the downward in the line.
Now I want to talk about the law of supply. In
this law of supply services or goods will sale in a certain point. The law of
supply is different with the law of demand, in this law of supply it’s curve is
upward sloping. It means when the price
of the good sold increase, the quantity will increase also. It also means the
higher the price the higher the quantity supplied. All of the producer will
supply more in the higher price because the higher the selling quantity the
higher the revenue. This is the law of supply.
After talking about the
supply, quantity supply, and law of supply, now is the demand turn. First, I
want to say about the demand. We can say that demand equal to the wants of
consumers. Demand is how much (quantity) of the product (goods and services)
that consumer wants to buy at a given price. The curve of the demand is sloping
downward it means when the price decrease the consumer will more willing to
purchase the product. In other hand
demand will facing many problem for example the price of the substitute and
complementary goods. Demand may be completely unrelated to price, or nearly
infinite at a given price. Along with supply, demand is one of the two key
determinants of the market price.(InvestorWords,2013). After the demand I want
to talk about the quantity demand. Quantity demand is how many of the product
that consumer willing to buy at a certain price. Quantity demand always related
with the price. It is known as demand relationship. Now I want to use few
figure to show out the differences between the demand and quantity demand.
figure(2.1) (Reem.H
, 2013). In this figure we can see that the demand curve is shifting to the
right and there are clearly show out the demand is increasing. In this point we
can know that when the demand is increasing the curve will shift to the right.
Opposite, when the demand is decreasing the demand curve will shift to the
left.
figure(2.2) This figure will
show more clearly about the demand curve. When the curve shift to the right as
D0 shifts to D2, it is showing out that increase in demand. When the curve
shift to the left as D0 shifts to D1, it is showing out that decreasing in
demand.
figure(2.3) This figure show
out the movement of the point of quantity demand in the curve and we can know
that . In this figure we can know that quantity demand is relationship with the
price, which is demand relationship. When the price of the product increase the
quantity demand will decrease and point of quantity demand will move downward.
Opposite that, when the price of the product decrease and the quantity demand
will increase and the point of the quantity demand will move to the downward. Now I want to explain about the movement of
the point of quantity demand. The point of the quantity demand is move along
the curve. This is about the quantity demand.
After the quantity demand I
want to write is law of demand. Law of demand is talking about , if other
factors remain equal, the higher the price of good, the less people will demand
the goods.
(Reem.H, 2013). In other words, we can say that the
higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded (Reem.H , 2013). When the
price of goods is high, it will make less people buy it, because if the price
rise, so does the opportunity cost of buying that good. Therefore people will
not to buy a product with a price that will force them in their life. This is
what we say the law of demand.
figure (3.1)(Martin.C, 2012)
In this figure we can see that the supply of diamond has drop nearly to 30%
since 2007 but the demand is growing the same percentage. It show out that when
the supply is decreasing the demand will increase at the same time because all
the people want to get it and it can sell in a higher price in this lack of
supply situation.
Reference:
BYU,(2013) Supply and Demand. Available from: http://courses.byui.edu/ECON_150/ECON_150_Old_Site/Lesson_03.htm
[Accessed 09 June 2013]
John.B, (2008) ECONOMIC
PERSPECTIVES. Supply vs Quantity Supplied[blog].
11 May. Available from: http://econperspectives.blogspot.com/2008/05/supply-vs-quantity-supplied.html
[Accessed
08 June 2013]
Martin.C
(2012) Diamond supply down 30%, demand up
30% – De Beers. Avialable from: http://www.miningweekly.com/article/diamond-supply-down-30-demand-up-30-de-beers-2012-08-15
[Accessed 08 June 2013]
Mike.M, (2013)Supply- The Economic of Supply.
Available from: http://economics.about.com/od/supply/p/supply.htm
[Accessed 08 June 2013].
Reem.H, (2013) Economic
Basics: Supply and Demand. Available from: http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/economics3.asp
[Accessed 08 June 2013]